Keywords: a bronchial asthma, vegetative nervous system, a heart rate variability, alarm, depression, emotional infringements, the vegetative status, psychosomatic diseases, the personSTUDYING OF THE VEGETATIVE STATUS, EMOTIONAL INFRINGEMENTS AND PERSONAL FEATURES AT THE BRONCHIAL ASTHMAOn this page there is an information on own scientific research which is devoted to studying of an emotional state, personal features and a vegetative regulation at patients with a bronchial asthma. Publications in various collections, and also the reports reported at conferences are submitted. O.S.Antipova Interrelation of a vegetative regulation with a level of uneasiness and depression, character of communicative behavioural reactions and with mechanisms of psychologic protection of patients with a bronchial asthma / O.S.Antipova, M.K.Reznikov // Pressing questions of psychiatry, an addictology and medical psychology. Release 6.-Voronezh: Publishing house the Cossack farm "Murom".-2004.-Pages 16-19. INTERRELATION OF THE VEGETATIVE REGULATION WITH THE LEVEL OF UNEASINESS AND DEPRESSION, CHARACTER OF COMMUNICATIVE BEHAVIOURAL REACTIONS AND WITH MECHANISMS OF PSYCHOLOGIC PROTECTION OF PATIENTS WITH THE BRONCHIAL ASTHMAthe Voronezh state medical academy of a name of N.N.Burdenko Faculty of psychiatry with an addictology, Voronezh The purpose of work was studying interrelation of a vegetative regulation of patients by a bronchial asthma with an expressiveness at them disturbing - depressive distresses, features of protective mechanisms and communicative behavioural reactions. On base pulmonologicheskih abjointings of the Voronezh regional hospital and the Voronezh municipal hospital ¹8 58 patients (25 men and 33 women) in the age of from 16 till 58 years (35,5±11,5 years) with serious (10) and average flow a bronchial asthma (48.) have been surveyedStudying emotional sphere was carried out with the help of procedure "TiD" estimating an expressiveness alarming and depressions. It has been secured two bunches of patients: I (n=37) - with the raised level of alarm and depression (less than 1,28 points); II (n=21) - with absence of uneasiness and depression (more than 1,28 points). It is important to note, that an expressiveness of emotional infringements of patients of bunch I basically, estimated as subclinical. For studying communicative behavioural patterns in disputed situations at 38 patients projective procedure Rozentsvejg was used. Mechanisms of psychologic protection estimated at 15 patients with the help of procedure " Life style index ". Vegetative tone was investigated with the help statistical and a spectral analysis of a heart rate variability with use of hardware-software complex "Varikard" 1.4. Among parameters of a heart rate variability from average size of RR-intervals (SDNN), a square root frequency of cardiac reductions, a standard deflection have been chosen from the sum of squares of a difference consecutive a steam of RR-intervals (RMSSD), stress-index (SI), total power (TP), and also three frequency ranges: HF (0,15-0,4 Hz), LF (0,04-0,15 Hz) and VLF (0,003-0,04 Hz). Patients of bunch I are authentically more often (rs=0,47, p<0,01) recognized a role of psychogenic factors in development of exacerbations a bronchial asthma. The exacerbation of disease descended, as a rule, in the situations demanding exhibiting of the responsibility, independence, independence or skill to go through grief and loneliness. The raised levels of alarm and depression authentically more often were observed at women that the data on the greater frequency of occurrence of alarming depression at women (confirm M.N.Bogdan, 1997; N.Breslau et al., 1998). On procedure Rozentsvejg at the majority of patients the prepjatstvenno-prepotent phylum of reaction in disputed situations prevailed and the expressed downstroke of self-protective type of reaction was marked. At 55,3 % of patients the behavioural orientation was taped impunitivnaja. Correlation interrelations between UT and UD and phylum of reaction in disputed situations it is not revealed. The leading phylum of psychologic protection of patients a bronchial asthma will consist in denying that information on the choronomic validity which disturbs and can result in the intrinsic conflict. The mechanism of denying is characteristic, basically, for persons of a hysterical depot and underlies their raised suggestibility and distortion of reality. It would be desirable to note, that in other our research (O.S.Antipova, O.N.Kulikova), concerning the teenagers, suffering a bronchial asthma, also leading phylum psychologic was denying. Besides the patients a bronchial asthma are more senior, the more distinctly at them in frame PZ reactive formations (hypercompensation) which essence will be were traced, that the person prevents expression of inadequate ideas for it, senses or acts by the exaggerated development of inverse tendencies. Differently, for indifferent or an agressive behavior of such patients the strong need for love and support frequently hides. In this connection, it is interesting to note, that frequency and gravity of disturbing - depressive distresses with the years accrued. Received on projective procedure Rozentsvejg and Life Style Index the data correspond to representations of other authors about specific personal features of patients a bronchial asthma. For asthmatics predilection to depressing choronomic exhibitings depression and aggression (P. Millett, 1978), low frustratsionnaja tolerance in a combination to the tendency to constrain reaction on frustratsiju (J.J. Groen, 1982) is characteristic. The raised personal uneasiness frequently experienced by the patient as causeless, is consequence of not realized intramental conflict between desire of love and tenderness, on the one hand, and pavor, izbeginiem them, with another (F.Alexander, 1951; G.B.Fedoseev, S.J.Kuprijanov, 1985; V.Brojtigam, P.Christian, M.Rad, 1999). Research problems included studying interrelation of a vegetative regulation with levels of alarm and depression, features of behavioural reactions in disputed situations, with an expressiveness of mechanisms of psychologic protection. On value of a pulse rate bunch I authentically did not differ (p>0,05) from bunch II, i.e. the average level of functioning of system of a circulation in both bunches was identical. At the same time, at patients with emotional distresses were authentically lower (p<0,05) than value of parameters SDNN (in bunch I - 56,8±25,4 ms, in bunch II - 82,4±33,1 ms) and TP (in bunch I - 4453±2891 ìñ2, in bunch II - 8726±4982 ìñ2), that testifies to decrease of the general heart rate variability and reflects intensity of regulation mechanisms and downstroke of adaptive opportunities. It proves to be true also higher values SI in bunch I (342,6±150,2 standard units) in comparison with bunch II (119,1±49,9), that reflects the tendency to a prevailation of the central adrenergic mechanisms at rising levels of alarm and depression. Besides at rising a level of alarm and depression it was marked statistically significant (p<0,05) downstroke parasimpaticheskih influences on a cardiac rhythm: in bunch I RMSSD compounds 50,0+29,7 ms, and in bunch II - 78,8+36,6 ms. In detail not discussing results of a spectral analysis, it is necessary to note, that the relative contribution of various frequency ranges to the general heart rate variability to bunch I and II essentially did not differ, that is, the pattern of interaction of various departments of a vegetative nervous system by a principle of " stressed counteraction " (M.N. Levy, 1971 was kept; A.M.Vayne, 2000). On the other hand, at presence of the subclinical expressed emotional distresses of a disturbing - depressive spectrum at patients a bronchial asthma the balance sympathetic and parasimpaticheskogo departments of a vegetative nervous system is characterized by intense interaction, the vegetative regulation becomes inert. Thus, at absence of disturbing - depressive exhibitings a vegetative regulation of patients the bronchial asthma differs the greater flexibility. Even soft, clinically undifferentiated emotional distresses, first of all, result in inactivity, intensity of regulation mechanisms and downstroke of adaptive opportunities of an organism. The phylum and an orientation of reaction in the disputed situations, revealed at inspection of patients on procedure Rozentsvejg, do not influence a vegetative regulation. At the same time, indirect statistically significant correlation interrelation between a degree of manifestation of a psychologic defense reaction of denying and parameters of the general heart rate variability (SDNN, TP) is defined. Direct correlation between an expressiveness of the mechanism " Reactive formations " and gravity of alarming and depressive exhibitings is revealed. The received data confirm not adaptive character of psychologic protection of patients a bronchial asthma, promoting formation of disturbing - depressive distresses and inactivity, intensity of regulation systems and downstroke of adaptive opportunities of an organism. THE REPORT AT CONFERENCE " THE STUDENT'S MEDICAL SCIENCE - 2004 "In a modern medical science integration of various disciplines that allows to survey this or that disease from the different points of view is observed. On modern representations a lot of pathogenic factors takes part in an etiology and a pathogeny practically any disease, the role of many of them is frequently underestimated. In particular, it concerns to psychogenic factors. The purpose of the present work was studying interrelation of an emotional state, features of psychologic protection of the person and phylum of reaction in disputed situations with character of a vegetative regulation at patients with a bronchial asthma. Research was carried out on base pulmonologicheskih abjointings of the Voronezh regional hospital and the Voronezh municipal hospital ¹8. In total 72 patients have been surveyed, their which the final report included 58 patients (25 men and 33 women) in the age of from 16 till 58 years (35,5 and * 177; 11,5 years) with serious (10) and average flow a bronchial asthma (48). Patients were excluded from research with a concomitant pathology which presence could affect results. Statistical processing results was carried out with the help of the program " Statistica for Win 6.0". Nonparametric criterion U the God-send - Uitni and criterion Spirmena for correlation analysis was used. Studying emotional sphere was carried out with the help of procedure "TiD" (JU.L.Khanin, 1976), estimating an expressiveness alarming and depressions. It has been secured two bunches of patients: I (37 patients) - with the boundary and raised level of alarm and depression (less than 1,28 points); II (21 patient) - with absence of uneasiness and depression (more than 1,28 points). It is important to note, that an expressiveness of emotional infringements of patients of bunch I basically, estimated as subclinical, and clinically expressed level of alarm / depression met only in 10 % of cases. 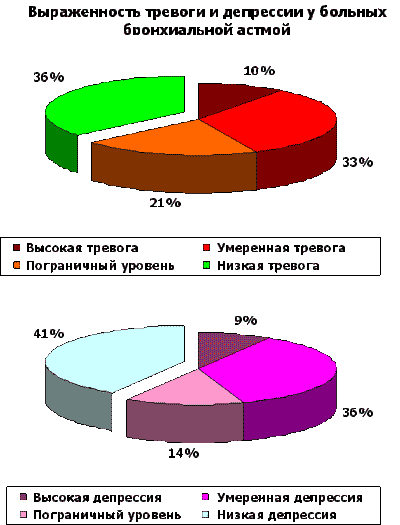 Patients with disturbing - depressive exhibitings are authentically more often (p*lt; 0,01) recognized a role of psychogenic factors in development of exacerbations of a bronchial asthma which were marked, as a rule, at household and industrial conflicts, and also in the situations demanding exhibiting of the responsibility, independence, independence or skill to go through grief and loneliness. The raised level of alarm and depression authentically more often was observed at women that the data on prevalence of disturbing - depressive infringements in dependence on a sex confirm. In our work studying a vegetative regulation of patients by a bronchial asthma was carried out. Vegetative tone was investigated with the help statistical and a spectral analysis of a heart rate variability with use of hardware-software complex "Varikard" 1.4. Among parameters of a heart rate variability from average size kardiointervalov (SDNN), a square root (pulse rate), a standard deflection have been chosen from the sum of squares of a difference consecutive a steam of RR-intervals (RMSSD), an index of a strain of regulation systems (SI), general vigor of a spectrum (TP), and also three frequency ranges frequency of cardiac reductions: HF (0,15-0,4 Hz), LF (0,04-0,15 Hz) and VLF (0,003-0,04 Hz). 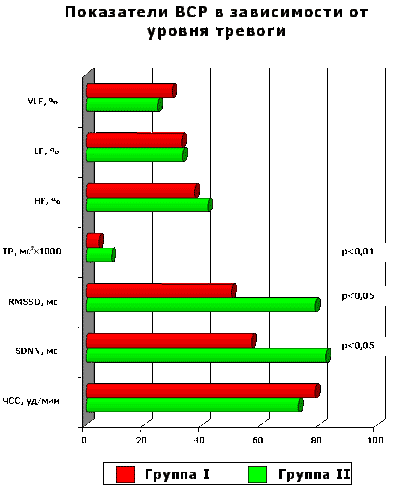 Research problems included studying a state of a vegetative regulation into dependences on a level of alarm and depression. On value of a pulse rate the bunch of patients with disturbing - depressive exhibitings authentically did not differ (p*gt; 0,05) from bunch II, i.e. the average level of functioning of system of a circulation in both bunches was identical. At the same time, at patients with emotional distresses of value of parameters SDNN (in bunch I - 56,8 and * 177; 25,4 ms, in bunch II - 82,4 and * 177; 33,1 ms) and TR (in bunch I - 4453 and * 177; 2891 ms2, in bunch II - 8726 and * 177; 4982 ms2) were authentically lower (p*lt; 0,05), that testifies to decrease of the general heart rate variability. Loss by a cardiac rhythm of the variability reflects intensity of regulation mechanisms and testifies to downstroke of adaptive opportunities of an organism. It proves to be true and is authentic higher values SI in bunch of persons with disturbing - depressive exhibitings (342,6 and * 177; 150,2 standard units) in comparison with other bunch (119,1 and * 177; 49,9), that reflects the tendency to a prevailation of the central contour of a regulation at rising a level of alarm and depression. It is interesting to note, that at rising a level of alarm and depression it was marked statistically significant (p*lt; 0,05) downstroke of parameter RMSSD that it is possible to treat, how downstroke of a heart rate variability as a whole, but the degree of downstroke of the given parameter does not allow to assert about decrease parasimpaticheskih influences. In I to bunch RMSSD - 50,0+29,7 ms, and in bunch II - 78,8+36,6 ms. In detail not discussing results of a spectral analysis, it is necessary to note, that the relative contribution of various frequency ranges to the general heart rate variability in I and II bunches essentially did not differ. Differently, at patients with a bronchial asthma with a various degree of manifestation of disturbing - depressive exhibitings character of a vegetative regulation did not variate. We count, that it is connected to presence of the mechanism, so-called " stressed antagonism " between sympathetic and parasimpaticheskim a department of vegetative nervous system. On the other hand, at presence at patients of the subclinical expressed emotional distresses of a disturbing - depressive spectrum, the balance sympathetic and parasimpaticheskogo departments of vegetative nervous system is characterized by intense interaction. For studying communicative behavioural patterns in disputed situations at 38 patients the projective procedure risunochnoj frustratsii Rozentsvejga was used. On the given procedure at the majority of patients the prepjatstvenno-prepotent phylum of reaction in disputed situations prevailed, and the expressed downstroke of self-protective type of reaction was marked. At 55,3 % of patients the behavioural orientation was taped impunitivnaja. To such people softness, compliance, disability to protection of own interests are peculiar, but such people "are sincere enough", have predilection to sympathy and empatii. The received results are compounded with the data of some authors (Mellet, 1978; Groen, 1982; Groen, Pelser, 1960) about predilection of patients with a bronchial asthma " to depress aggression ", " to constrain reactions on frustrirujushchee influence ". In our research it is not revealed correlation interrelations between a level of alarm and depression and phylum of reaction in disputed situations. 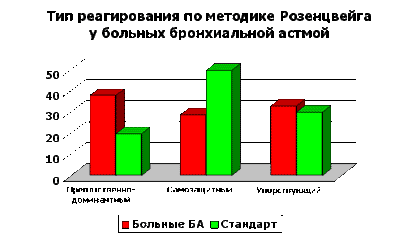 Mechanisms of psychologic protection of the person estimated at 15 patients with the help of procedure " the Index of zoetic style ". As a whole, at patients with a bronchial asthma predominance of two phylums of protection has been revealed: "Denying" (a mean score 74,7; 67 % of patients had parameters over 80 points) and " Reactive formations " (a mean score 73,1; 47 % had very high parameters). By means of the mechanism of protection "Denying" the person denies circumstances invoking alarm, or imperfection of the personal qualities. Usually such patients have a hysterical personal radical. At persons with the expressed mechanism of psychologic protection "Denying" downstroke of the general heart rate variability is marked.  The mechanism " Reactive formations " in essence represents an overcompensation - the person is not realized aspires to prove in such spheres where she feels herself weak. The expressiveness of this psychologic protective mechanism was various in dependence on age of patients. In an age-grade till 30 years the expressiveness of " Reactive formations " - 39,8, and in bunch is more senior than 30 years - 89,7. In this connection, it is interesting to note, that frequency and gravity of disturbing - depressive distresses with the years accrued, that is the combination of an expressiveness of an overcompensation to a level of alarm and depression is traced. I shall result a clinical example: patient Í., 50 years. The experience of disease - 5 years. The ancestral burdeness of the patient is denied. The cause of the disease sees in a combination of 2 factors: a chronic bronchitis and the factor traumatizing psychics. Particularly the patient to speak about a mental trauma has refused, marks only, that it was the long conflict to its parents. During that moment she characterizes the state as follows: " Has swallowed insult … could not react to not offend elderly parents ". Approximately in 2 weeks after the beginning of action of this situation traumatizing psychics it had a first attack of a bronchial asthma. Each attack began with loss of an olfaction, was accompanied by the pavor expressed by disturbing. Now among other factors provoking an attack specifies the factor traumatizing psychics. Itself characterizes as sensitive, but at the same time the "not scandalous" person - " reconciles all ", concerning the touchiness figuratively marks, that " the word means more, than something ". Complains, that " there is no free, unchained life ", because of impossibility " freely to breathe ", from time to time there is a sensation that "does not live" or " lives, as at station ", " there is no future ". On Rozentsvejg - relative rising prepjatstvenno-prepotent and downstroke of self-protective type of reaction. Level of alarm - boundary (0,22), a level of depression - clinically expressed (-8,83.) Summing up, it is necessary to present the basic conclusions of the given work. It is found out, that at absence of disturbing - depressive exhibitings the vegetative regulation of patients with a bronchial asthma differs the greater flexibility. At the same time, even soft, subclinical emotional infringements result in inactivity and intensity of regulation mechanisms, that, results in downstroke of adaptive opportunities of an organism. Thereof at such patients it is possible to assume low efficacyy of the basic therapy. The phylum and an orientation of reaction in disputed situations do not influence a vegetative regulation. The interrelation between a degree of manifestation of a psychologic defense reaction of denying and downstroke of parameters of the general heart rate variability (SDNN, TP) is defined. Direct correlation between an expressiveness of the mechanism " Reactive formations " and gravity of alarming and depressive exhibitings is revealed. The received data evidently show not adaptive character of psychologic protection of patients with a bronchial asthma, show a role of situations traumatizing psychics and an emotional state in flow of a bronchial asthma and testify to necessity of system engineering of psychotherapeutic actions. Reznikov M.K.research of personal features and the vegetative status of patients with a bronchial asthma / M.K.Reznikov, O.S.Antipova // Proceedings of 4-th international scientific - practical conference " Health and Formation in XXI blepharon " on May, 23-25, 2003. Moscow, 2003.-Pages 524-525. RESEARCH OF PERSONAL FEATURES AND THE VEGETATIVE STATUS OF PATIENTS WITH THE BRONCHIAL ASTHMAThe purpose of work was studying features of the psychologic and vegetative status of patients by a bronchial asthma. 32 patients a bronchial asthma in the age of from 17 till 58 years (middle age 38,4 and * 177 have been surveyed; 10,6 years). From them 19 men and 13 women. At 25 patients - an average bronchial asthma, at 7 - a serious degree a bronchial asthma. Duration of disease from 1 till 25 years. Patients were excluded from research with chronic diseases of other systems of members which presence could affect results. For research of emotional sphere procedure "TiD" (by Hanin J.L., 1976), determining a level of alarm and a level of depression was used. For an assessment of behavioural patterns in stressful situations projective procedure Rozentsvejg on which 3 types of reactions (TP) are taped was used: prepjatstvenno-prepotent (OD), self-protective (ED) both persisting (NP) and 3 orientations of reactions: ekstrapunitivnaja, intropunitivnaja and impunitivnaja. Research of the vegetative status was carried out at 19 patients with the help of time analysis heart rate variabilities (heart rate variability). Ritmogrammy were recorded with the help of programno-apparatus complex "Varikard" 1.4 on standard procedure in a state of rest. Also influence of psychogenic factors in development of an attack a bronchial asthma from words of the patient was taken into account. Statistical processing was carried out with the help of criterion U the God-send - Uitni. As a whole in bunch of 65,6 % of patients marked an appreciable role of the psychogenic factor, as provoking an attack. Authentic differences in levels of alarm and depression in various age-grades are revealed. Young patients (till 30 years) are characterized by minimum levels of alarm and depression (0 % and 12,5 % of patients with the expressed level), and most frequently clinically expressed level of alarm and depression (61,5 % of patients) meets in bunch of sick 41-50 years. On procedure Rozentsvejg in comparison with standard sizes downstroke of expressiveness ED for all patients is characteristic, and at 84,4 % of patients rising OD - a parameter frustrirovannosti is taped. Taking into account combination TP with HP, it fixed, that at 62,5 % prevailed OD phylum of reaction in a combination with impunitivnoj a behavioural orientation. For revealing a prevailing department vegetative nervous systems (vegetative nervous system) we have divided patients into 2 bunches by criterion SDNN - to a parameter of the general variability. Bunch I included patients with SDNN less than 40 ms (52,6 %), in bunch II - patients with SDNN more than 40 ms (47,4 %). On R.M.Baevskomu, downstroke SDNN is lower 40 ms typically for patients with a relative prevailation of tone of a sympathetic department of a vegetative nervous system that proves to be true authentic changes of a pulse rate (p*lt; 0,05), RMSSD (p*lt; 0,01), SI (p*lt; 0,01), TP (p*lt; 0,01) (see tab.)
From the table it is visible, that in bunch I SI=606,3 in c.u. that testifies to the expressed intensity of regulation systems. At patients in bunch I it is authentic (p<0,01) above levels of alarm and depression in comparison with bunch II. That fact is interesting, that the quantity of women in bunch I has made 60,0 %, while in bunch II - 10,5 %. In bunch I of 70,0 % of patients recognized the important role of psychogenic factors in provocation of attacks a bronchial asthma, and in bunch II only 44,4 % have attributed psychogenic the factor to provoking. Conclusions. Thus at the majority of patients a bronchial asthma such personal features as softness, compliance, emotional restraint, the parameter frustrirovannosti is raised are taped inherent OD in a combination with impunitivnoj an orientation. These data can be used at psychotherapeutic correction of patients. At persons with predominance of sympathetic tone (it is women more often), disease is accompanied by the greater dependence on psychogenic factors, such patients imejutsklonnost to formation of disturbing - depressive distresses, for them the state of a strain of regulation systems of an organism is characteristic. To discuss a material at a forum of a site Keywords: a bronchial asthma, vegetative nervous system, a heart rate variability, alarm, depression, emotional infringements, the vegetative status, psychosomatic diseases, the personMain | Abstracts, compositions, lectures | Psychiatry | Links
|