THE CASE HISTORY ON THERAPYthe DIAGNOSIS: the Chronic hypotonia of gizzards
REGISTRATION
THE ANAMNESIS OF LIFE (Anamnesis vitae)From words of the attendants, the animal in the Ekaterinburg circus is 4 years. The leaving good contains in a room, an exercise in the street is rare, participates in the circus program (now 3 times day on representation). Roughages (hay), juicy foods enter into a ration (carrot, a potato, beet, cabbage), concentrates. THE ANAMNESIS OF DISEASE (Anamnesis morbi)The camel within 20 days refused meal and water. In the beginning it did not invoke disturbing as at the given kind of animals long hunger-strikes can be connected to physiological features, and Def periodically without harm for health refused meal within 10-14 day then again ate normally. However this time the camel has ceased to work, has become more to lay, has lost interest to world around. THE CONDITION OF THE ANIMAL AT THE MOMENT OF RESEARCH.the General research.Date on December, 13, 2000. Temperature 37,7 and * 730; About Pulse of 72 impacts in one minute. Respiration 12 in one minute. A habit: a constitution correct, the constitution dense, a position of a body in space lentic, temperament phlegmatic, temper kind. The leather elastic, moderately damp, integrity of her is not broken. An odour specific. The wool rich, covers all seen plots of a body of an animal, a wool dim, is well kept in a leather. Humps empty, hang down emb. Submandibular lymph nodes mobile, painless, a dense consistence, the aboriginal temperature is not enlarged. The mucous membrane of a mouth and a conjunctive of pink colour, dry, integrity is not broken. Research of separate systems. Cardiovascular system:arterial pulse rhythmical, mild, average. Jugular veins elastic, fluctuations are absent. A cardiac impulse weakened, character diffuse. The cordial range is painless. Cordial tints are muffled, leveled. Respirationgrudo-belly type, rhythmical, moderate. Wings of a nose move at respiration, the expirations are absent. The range of a larynx and trachea is painless, the aboriginal temperature is not raised. The chest wide, is painless. System of digestion: appetite is absent, the animal gnashes tooths. An eructation infrequent, a sialosis diminished. The cud infrequent, rigid, stinking, a camel spits out a cud. Tongue is impose, without damages. Tooths in a measure are erased. From an oral cavity a unpleasant odour. A position of a neck free. The range of a gullet is painless, a swallowing free. Salivery glands not enlarged. A belly tighten, it is symmetric. Hungry fossas sunk down, reductions of rumen sluggish, ruminatsii 2 times 2 minutes. At a percussion of range of rumen a blunt note. At an auscultation peristaltic hums are absent. A defecation infrequent, the faecal matter fine, is coated with slime. Urino-genital system:outside sexual organs without damages, correspond to a kind and a sex of an animal. A urination infrequent, painless, the oliguria is marked. Colour wet dark yellow, urine rich, transparent, has a specific odour. Sense bodys:eyes pure, reaction of pupils to light alive, sight is kept on both eyes. Cochleas are kept, the profile is not changed, the expirations are absent. The ear is kept on both ears. The taction is kept. Nervous system: the general condition depressed, animal is apathetic, weak reaction on environmental. A coordination of locomotions correct. Tactile and pain sensitivity are kept. The profile of a skull and a spinal column is not changed. A condition of a mineral exchange: a tail of a straight line, there are last tail vertebra. Last edges resilient, intercostal spaces normal. LABORATORY RESEARCHES.the Blood analysiswas carried out in laboratory of a clinical immunology of faculty of contagious and invasion diseases UrGSHA. A findings of investigation:
Research wetit was carried out visually and with use of diagnostic strias HEXA-PHAN. A findings of investigation: urine transparent, dark yellow colour, with an acute odour, quantity wet, secreted for one portion, insignificantly.
Research of a faecal matteron eggs of helminths was carried out in Regional veterinary laboratory, result negative (see. The appendix, examination ¹ 322) THE DIAGNOSIS:A chronic hypotonia of gizzards. Hypotonia rumis et reticuli chronica. THE FORECAST:Congenial. THE TREATMENT PLANNING:
DIARY KURATSII
the OUTCOME:convalescenceDYNAMICS OF TEMPERATURE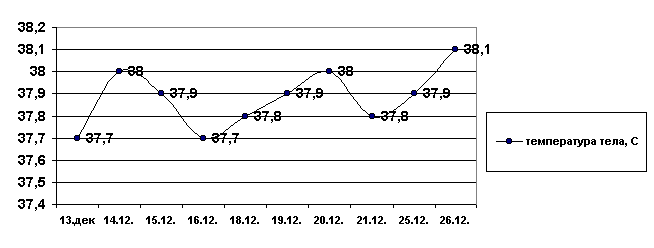
DYNAMICS OF PULSE AND RESPIRATION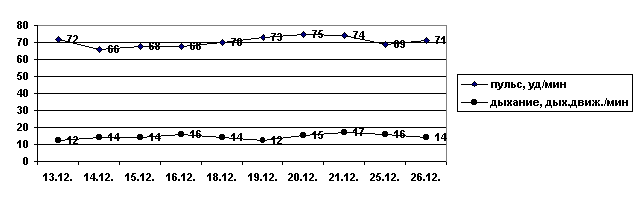
DYNAMICS RUMINATSY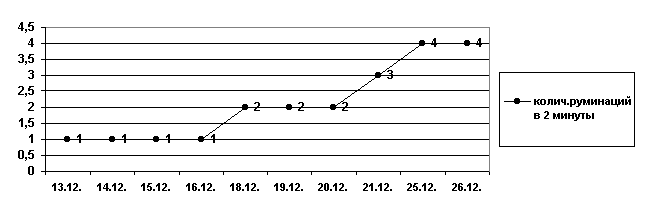 the Hypotonia of gizzards (Hypotonia rumis et reticuli chronica) - the disease described by distress of motor activity of gizzards and showing dropping of a tonus of a muscles of rumen, the manyplies and a grid and reduction of frequency of their reductions. Can proceed it is acute and chronic, by origin to be initial and secondary (4, 7). the Etiology.More often the cause of a hypotonia is infringement of regulations of a feeding of an animal: at a uniform feeding, at a ratio distortion in a ration rough and juicy foods, at a feeding to an animal of substandard forages. Contributing factors are absence of an awake exercise, a disadvantage of a drinking water, stressful conditions of animals at constant change of a situation (6). In the chronic form disease meets as continuation acute if not his causes or etiological factors frequently are eliminated repeat. Disease can flow also in an atonia - complete loss of a tonus of a muscles of gizzards and, hence, them sokratitelnoj abilities (4). Secondary hypotonias and an atonia educe owing to dropping a resistance of animals and weakening of a tonus of a muscles at many contagious, invasion and noncontagious diseases (4, 6, 7). the Pathogeny.Etiological factors reduce an excitability and sokratitelnuju ability of gizzards, break moving and evacuation of fodder masses to underlaying departments. Fodder masses slezhivajutsja, there is their decomposition to education of a plenty of toxic substances which, being absorbed in blood, invoke an intoxication, oppression of a central nervous system. Besides secreted toxins can cause an inflammation of a wall of a gizzard. In rumen the quantitative and qualitative structure of a microflora, a ratio of flying adipose acids, shift of the kislotno-basic balance aside an acidosis, infringement of synthesis of vitamins of group In (6,7) variates. The data of the hematological analysis show a leukocytosis, a neutrophilia and an insignificant lymphopenia that can specify development of inflammatory process in rumen and oppression of immune system (5.) the Diagnosis and the differential diagnosis.the Diagnosis in this case has been put on the establishment of the data of an anamnesis (the content and a ration of an animal) and clinical research (infringement of a cud and an eructation, downstroke sokratitelnoj to ability of rumen). Unfortunately, it was not represented possible to lead selection of cicatrical contents for acknowledgement of the diagnosis as the camel and in a fixed condition was capable to show resistance. With a strong percussion test has been lead to ranges of a xiphoid cartilage for exception of a traumatic reticulitis (result negative). A corking of an esophagus have excluded, as introduction of Tinctura Araliae of a false hellebore has caused appearance of a stinking eructation. Research of a faecal matter has excluded parasitosises. Treatment.After statement of the diagnosis to an animal the hungry diet and massage of range of rumen has been appointed. The lavage of rumen and a rate of cicatrical contents from the able-bodied camel was not represented possible, therefore the given methods at purpose of treatment have excluded. In quality ruminotornogo a means applied Tinctura Araliae of a false hellebore vnutrivnutrivenno in a dose of 4 ml in a normal saline solution. However in 10 minutes after introduction at an animal the stinking eructation which spurted has appeared has taken place a sharp respiratory depression, a muscle tone oslab, the camel has fallen. To putting off of undesirable reaction applied a solution of an atropine of a sulphate. Further from application of a false hellebore have refrained, therapy, basically, has been directed on putting off of an intoxication and a stimulation of activity of cardiovascular system. For a desintoxication solutions of a glucose of 5 %, an ascorbic acid, a chloride sodium of 0,9 % were used. In this case it would be expedient to apply hypertonic salt solutions of salts to normalization of motor function of a gastrointestinal tract (a calcium chloride, a chloride sodium), however in spent treatment of 10 % solution CaCl2was applied unitary, therefore could not render the therapeutic action. As a means excitant respiratory and cordial activity applied Cordiaminum subcutaneously in a dose of 6 ml on introduction, to augmentation of an energy potential of a cardiac muscle - Riboxinum vnutrivnutrivenno in a dose of 10 ml on introduction. In connection with that at a hypotonia synthesis in a gastrointestinal tract of vitamins of group is broken In and, in particular, In12, to a camel intramuscularly in a dose of 10 ml the solution of a cyanocobalamin has been appointed to introduction. Solutio oleosa of vitamins And and E (aekol) applied inside basically to humidifying and greasing of mucous membrane of a gastrointestinal tract. In this case, in my opinion, application of antibiotics since disease, to all attributes, was not contagious nature has not been justified and application of antibiotics could aggravate a dysbacteriosis in a gastrointestinal tract. Also purpose of Dexamethazonum since direct indications to application were not was unreasonable, and the given preparation is strong enough synthetic gljukokortikosteroidam and appoint it with guard, gradually reducing a dose, strict courses. One of his side effects is the immunodepression, and parameters of the relative content of lymphocytes in the leukocytic formula already specify failure of the given cellular link. Prophylaxis of disease.as a prophylactic measure only correction of a ration of a camel with the count of requirements for nutrients, forages and physiological features of his digestion in this case can serve. However it is difficultly feasible and, taking into account age of an animal, and time, which camel contains in a circus, can not result in desirable results. BREEDINGSThus, during kuratsii an animal the following observations and breedings have been made:
the LIST of the USED LITERATURE
To discuss a material at a forum of a site Main | Abstracts, compositions, lectures | Psychiatry | Links
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||